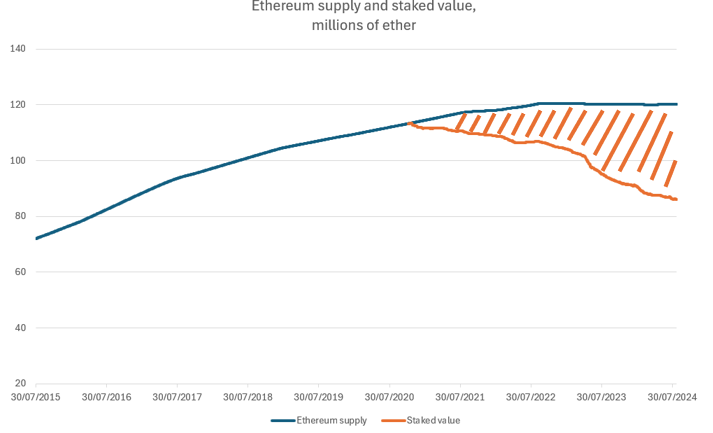
Over the past few years, since the transition to a Proof-of-Stake network, Ethereum has seen a consistent increase in staking volumes. The total amount staked has now risen to approximately 34 million ETH, accounting for 28% of the total ETH supply. This is, however, still low compared to other PoS blockchains, where more than half or even, in some networks, 90% of tokens are staked.
During this period, the reward rate for staking has decreased from around 4.4% to 3%. This is typical in proof-of-stake blockchains, where there is a negative correlation between the amount of staked tokens and the reward rate. As more tokens are staked, the network can reduce rewards since its utility and security are already well-supported.
Besides the native staking rewards, there are numerous DeFi instruments available that offer additional yields for ether holders.
Lido, a leading liquid staking provider that issues stETH to represent staked ETH, currently facilitates about one-third of all staked ETH. Holders are using stETH across various DeFi platforms to secure even higher yields, on top of their regular staking yield. For instance, protocols like EigenLayer and Symbiotic have been enticing stETH stakers with airdrops, making these options particularly lucrative.
Money or Speculative Asset?
Interestingly, despite these robust staking figures, Ethereum’s price performance has been modest compared to other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Solana. This testifies that ether's price is more affected by the trading (speculative) market forces rather than monetary economic rules.
The total supply of ETH has been stable since 2022, while staking has brought the cryptocurrency in circulation to the same levels as in 2017. Nevertheless, this has not affected the price of ether.
Instead, ether's underperformance may be linked to several factors, including the recent launch of Ethereum ETFs. Notably, the Grayscale ETF has predominantly seen outflows, leading to substantial selling pressures on the market.
Additionally, the tokenomics of Ethereum was affected by the Dencun upgrade implemented on March 13, which involved the introduction of nine Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), including EIP-4844. This upgrade significantly reduced the fees Layer 2 networks pay to process transactions on Ethereum Layer 1, enhancing the user experience on these networks but also decreasing Ethereum’s revenue from fees and its reward rates.
It also resulted in the transition of Ethereum from being deflationary to inflationary. Whether that was the developers' plan or simply a side effect, it remained to be observed.
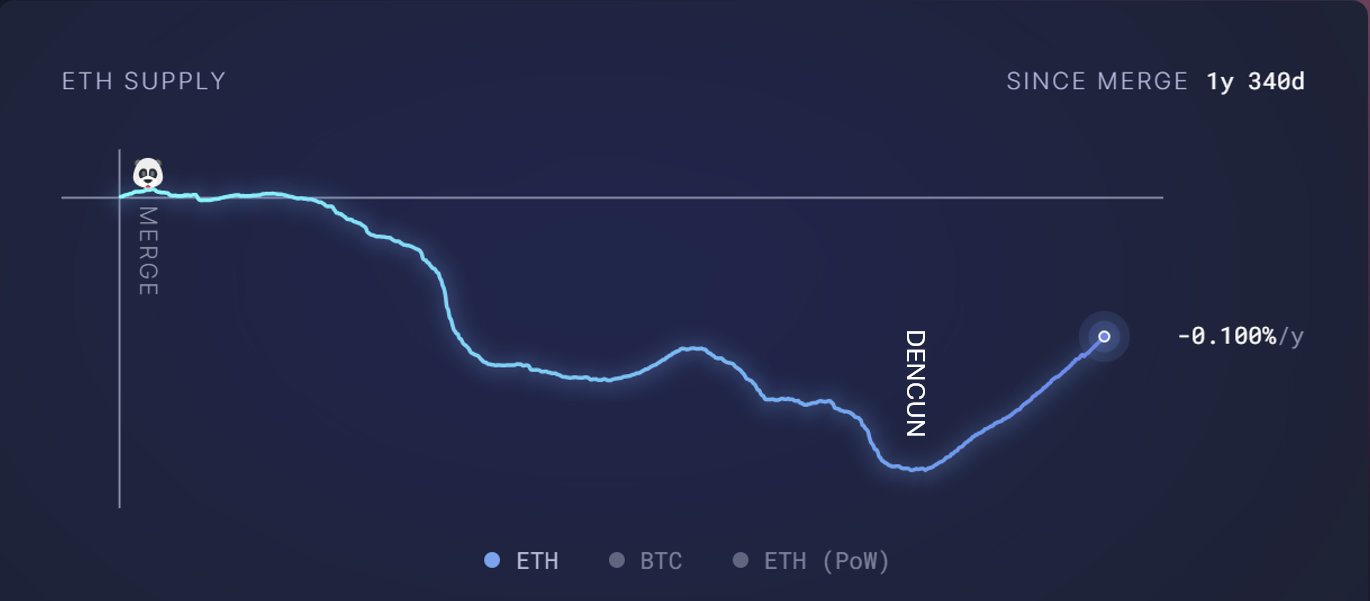
These factors have contributed to Ethereum’s current weakness more than the fundamental scarcity from staking locks.
As far as the speculative price is concerned, Ethereum’s short- to medium-term outlook heavily depends on broader crypto asset market trends. Should the market shift to a bullish stance, Ethereum is likely to benefit and potentially see an uptick in value.
Ethereum also possesses the most vibrant and continuously expanding ecosystem in the cryptocurrency space, featuring the largest number of projects and developers. Therefore, in the long term, we might observe the quality of these developments reflected in ETH’s price.

